As a follow-up to Todd’s post on using GPS in Jordan, here are the steps my brother used to turn his iPhone into a navigation system. On a trip to Lebanon two years ago, we were able to use my brother’s iPhone as a GPS. His iPhone is an unlocked GSM (meaning that he could swap out SIM cards—this is important!).
1. At the airport in Beirut, my brother purchased a SIM card and a T-Mobile 3G+ data plan in Lebanon. For our two-week trip, 2GB of data was sufficient, as long as we avoided using apps such as Google Earth which load image tiles every time you swipe or zoom. This near-constant loading of raster images really gobbles up data.
2a. While within the city of Beirut, my brother discovered that Apple Maps worked better. (Location Services has to be enabled.) It updated our present location faster and with greater precision than other apps, which was quite important in the city so that we did not miss any turns. The street maps in Apple Maps are vector data, so they loaded quickly. The problem with Apple Maps was that road names were in Arabic, so not easy to read. But, since we knew our destination, and we could see where we were at that moment, we could figure out which roads to take.
2b. Outside Beirut on the way to the next city, Google Maps worked better. Google Maps did not update our position as quickly, but it did show more of the smaller roads (very helpful!) and was pretty accurate. The street maps in Google Maps are also vector data, so the maps loaded quickly.
2c. Once we were within a mile or so of whatever obscure site that we were trying to find, my brother used OpenStreetMap within the app GaiaGPS. (GaiaGPS is $20 in the App Store; it works on both iOS and Android phones.)
As Todd did, before leaving on our trip, we located all sites in Google Earth. The Google Earth kml file was converted to a gpx file using the free kml2gpx website. My brother then loaded the gpx file into GaiaGPS. As with Google Maps, OpenStreetMap also showed more of the smaller roads and showed where our Google Earth site was located in relation to our position. Because OpenStreetMap is tile-based, sometimes it took the maps a little longer to load. To get around this, we could cache our route the night before, though sometimes we did not always know exactly which roads we would be using, or we did not cache all the zoom levels that we needed. GaiaGPS was not quite as fast at updating our position as Google Maps, but my brother could force GaiaGPS to update simply by snapping a photo within GaiaGPS. (Since GaiaGPS geotags photos, taking a photo forced GaiaGPS to update our location in order to write the coordinates to the jpg image file.)
3. We also used GaiaGPS to store waypoints. In essence, this feature kept track of the path we travelled by recording GPS coordinates every few seconds. Once we returned home, we were able to use the waypoints (a gpx file) from GaiaGPS to geotag all my photos using the free COPIKS PhotoMapper. The COPIKS app marries waypoint coordinates with a photograph based on matching timestamps. (It is important beforehand to sync up the date-time on your camera with the date-time on the iPhone.) COPIKS then writes the coordinate data to the jpg image file.
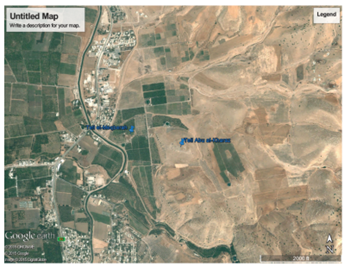
4. As Todd did in Jordan, we found screen captures from Google Earth to be helpful on several occasions. Rather than printing them, we loaded the images onto an iPad for reference.

 Pictorial Library of Bible Lands helpful for its list of coordinates as well. If you are looking for a GE file (kml) of lots of biblical sites in Israel and/or Jordan, search on the web (though reliability varies).
Pictorial Library of Bible Lands helpful for its list of coordinates as well. If you are looking for a GE file (kml) of lots of biblical sites in Israel and/or Jordan, search on the web (though reliability varies).