For an introduction to this series see here.
It seems only a short time ago that archaeologists were saying that there were only 3 positively identified 1st century CE synagogues in Israel – Herodion, Masada and Gamla (See “Synagogues” in Anchor Bible Dictionary, Meyers 1992: 6.255). In the case of Herodion and Masada – these are relatively late synagogues as they were both converted from Herodian structures during the first Jewish Revolt (66-73 CE). The Gamla synagogue represented the only tangible archaeological evidence of a synagogue built for the primary purpose of being a synagogue (versus later retrofitting).
The 2009 discovery of the first century CE synagogue at Magdala changed that perception. We have discussed this discovery on several occasions, including a debate regarding the function of the building and the possibility of excavating at the site with costs covered by the excavation. I asked on a recent visit and this offer still stands, according to the staff at the site. Also from what I gathered their work will continue long after 2013, as they had stated previously – see here for pictures of volunteers from fall 2012.
View Secret Places: BiblePlaces in a larger map (toggle between different map view in top left corner – other views might provide easier driving directions)
Getting to the first century remains at Magdala is quite simple – from Tiberias it is a mere five-minute drive to the north of town – make a right at “Magdala Hawaii” and turn into the construction site – there will be a sign that says “Magdala” and two small office buildings on each side of the road in front of the excavations.
Touring Suggestions
Upon arrival you will be met by a security guard who will ask you to donate money to the project (there is no admission fee) – he will also give you instructions on where you can and cannot go on the site. The guard might also offer a few words of insight about the site – take what he says with a grain of salt. The following instructions are tentative as visiting protocols will change as the Magdala Center project develops (for comparison note the complete absence of buildings in this area in the Google Maps view above).
Update 4/8/2013 – Entrance information: Opening time Monday-Friday 8-1pm. Email contact (HT: Shmuel Browns)
Historical Background and Discussion
Magdala means tower (Hebrew – migdal). It is never mentioned by name in the Gospels, rather the site name only appears when identifying Mary Magdalene apart from the other Marys (e.g. Matthew 27:56). Had the other Marys been named Salome instead of the ubiquitous “Mary” it is likely that even “Magdalene” would not be part of the New Testament record.
Before the founding of Tiberias as capital of Galilee in 20 CE under Herod Antipas, Magdala (Josephus calls the site Taricheae, which means fish) was the main administrative center (toparchy) of eastern Lower Galilee beneath the authority of Sepphoris, Antipas’ Galilean capital. In 20 CE, the capital shifted from Sepphoris to Tiberias and Magdala lost its administrative significance, but remained an important site. Later on in the 50s CE the site was ceded to Herod Agripa II (son of Agrippa I, grandson of Aristobolus, great-grandson of Herod the Great) and later still in 66 CE it was the site of a naval battle between the Romans under Vespasian the result of which was the total defeat of the Jewish forces (including the execution of thousands inside the stadium at Tiberias). This naval war also produced one of the most interesting archaeological finds of all-time – the so-called “Jesus Boat,” which probably owes its exceptionally rare preservation to the unique events that transpired during the onset of the first Jewish Revolt. (For more information regarding Magdala’s historical background see James Strange “Magdala Magdalene,” Anchor Bible Dictionary 4:463).
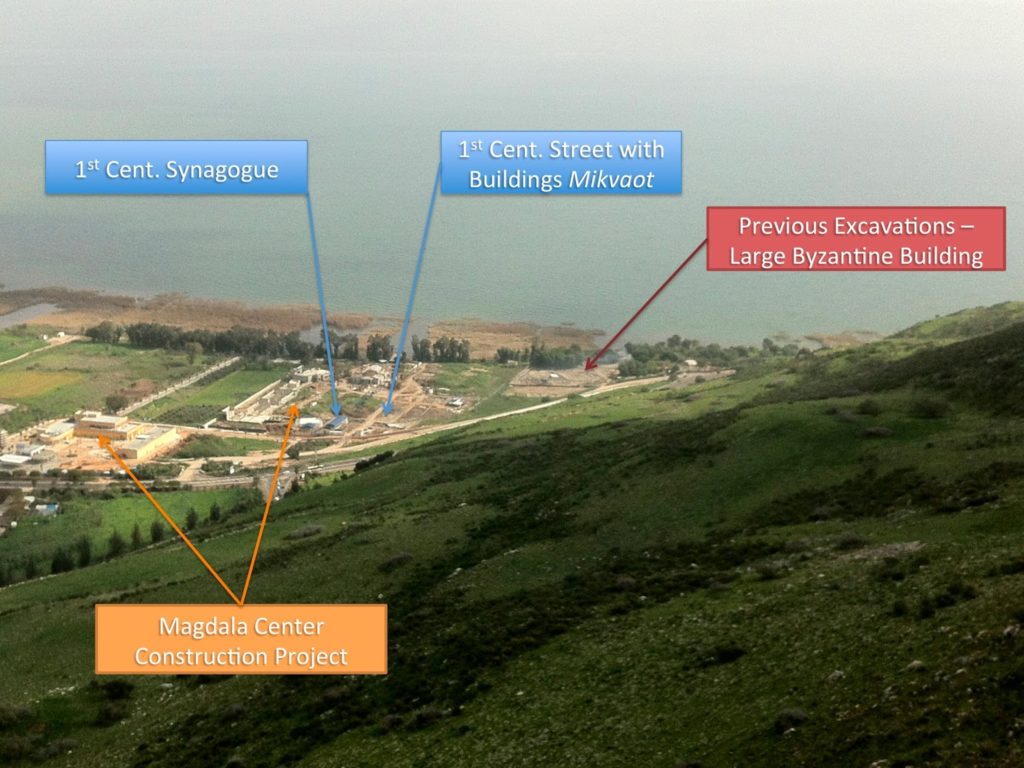 |
| Magdala from the eastern side of Mt. Arbel looking east towards the Sea of Galilee |
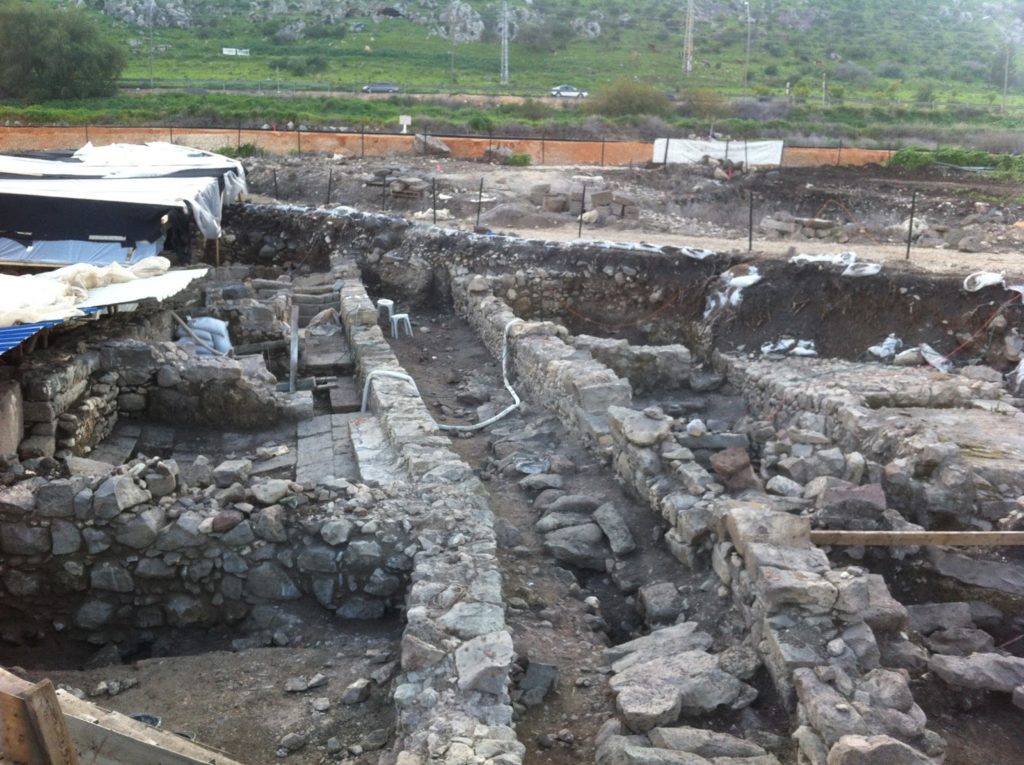
The synagogue is on the left side of the road, as of March of 2013 visitors could still not go into the synagogue itself, but you will be able to view the beautiful synagogue from a distance. As fascinating as the synagogue is – what caught my eye was the extremely well-preserved, presumably first cent. CE street ca. 30 meters south of synagogue (see picture above). Along this street one can easily make out several mikvaot (ritual baths) that seemed to be fed by means of a canalization system and remains of the foundations of buildings constructed from basalt (black volcanic rock typically used in construction in the Golan Heights).
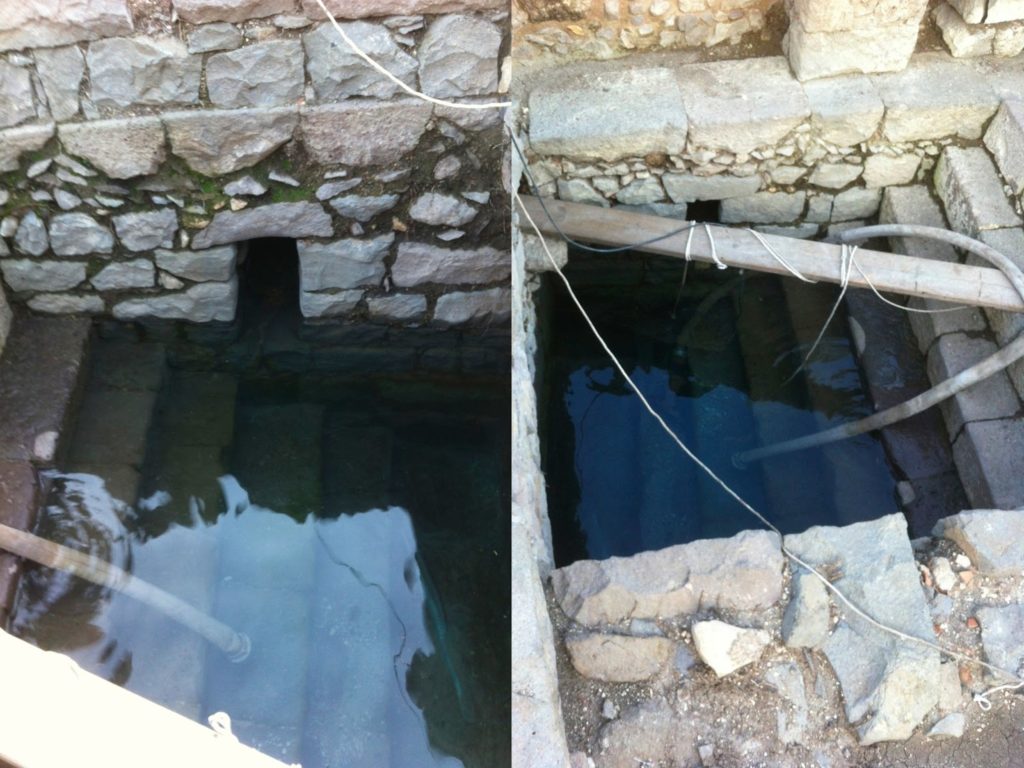 |
| Mikvaot? There are at least four of these along this street, notice the extremely well-preserved steps and opening for presumably filling the pool. |
While final say will go to the excavators of this important site, it seems quite clear that the remains around the synagogue, including the street with presumed mikvaot, all date to the same time period – the excavators have claimed that the synagogue is first century CE on the basis of coinage and pottery. It therefore seems likely that the connected buildings date to the same time period. Beyond the clear connection of this site to Mary Magdalene of the Gospels this Early Roman town has the potential to illuminate many details of first century, Galilean village dynamics.
In conclusion, this exciting new site should be considered a “required” stop on any trip to Israel that makes it to the Sea of Galilee. In the opinion of this author, Magdala is a more important site for folks interested in New Testament and Second Temple Judaism than say, Tabgha or Chorazin (primarily 4-5th cent. CE Byzantine remains with New Testament textual connections). Magdala has the potential of illuminating our understanding of first century daily village life (i.e. the very time of Jesus’ ministry) in the same way that Qatzrin has illuminated our understanding of everyday Jewish life in Mishnaic/Talmudic times.