The first stage of the archive is now available online, but my first impression is not positive. The viewer is clunky and the server is slow. They’ve also made it difficult to save any of the files for personal study. Perhaps improvements will come; the project is certainly a worthy one. Here’s the full press release from the Israel Antiquities Authority:
The archaeological archive of Israel, which is administered by the Israel Antiquities Authority and amasses data on all of the activity of the archeological entities in the country, is computerized and will go online in the coming days. This is being underwritten with joint funding provided by the
“Landmarks” heritage program in the Prime Minister’s Office and the Israel Antiquities Authority.
The scientific archive has its beginnings in the British Mandatory Department of Antiquities. It was
continued by the Israel Department of Antiquities and is managed today by the Israel Antiquities Authority, which invests considerable thought and resources in its operation. [Yes, they really said that about themselves!]
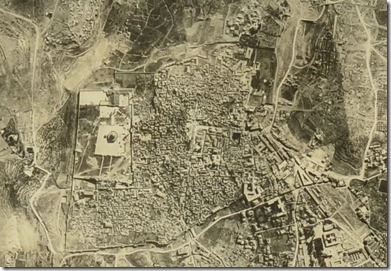
The first stage, containing tens of thousands of documents, photographs, maps and plans from the years 1919–1948 from Akko and Jerusalem, is already available for viewing online at www.iaa-archives.org.il. Most of this material was written in English.
Uploading the old and valuable material to the website required special preparations. In order to scan the material, the Israel Antiquities Authority engaged the services of ImageStore Systems Ltd. This is because the archival material is especially delicate and sensitive and cannot be scanned with industrial equipment; rather it can only be done individually and manually. The documents in the archive include texts photographs, maps, and plans etc. on many different kinds of paper.
According to Israel Cabinet Secretary Zvi Hausner and Reuven Pinsky, director of the heritage project in the Prime Minister’s Office: “The Mandatory archive constitutes the principal foundation of archaeological research of the past one hundred years. This program, as part of the Israel Archives
Network project for scanning and digitalization of the material on file in the archives, will make it possible for the public in general and particularly scholars in Israel and abroad to access these resources of knowledge”.
According to Dr. Uzi Dahari, Deputy Director of the Israel Antiquities Authority, “The scientific importance of the archive is invaluable, and it is the only one of its kind in Israel and in the world. In Israel there are approximately 30,000 known and declared antiquities sites that constitute our cultural heritage – the largest and most important asset of the State of Israel. The Israel Antiquities Authority declares, treats, surveys, and researches the antiquities sites in the country. One of the many activities of the Israel Antiquities Authority is the management and running of the scientific archive. The Israel Antiquities Authority decided to transfer the archive to the digitalized media, in order to disseminate the information throughout the world”. To this end, all of the information was scanned and it was indexed according to rules that are suitable for research needs”.
According to Ephraim Reich, director general of ImageStore Systems Ltd., “We are proud to have been given the opportunity by the Israel Antiquities Authority to take a significant part in preserving this important information for the public. The utilization of advanced technology for the purpose of accessing enormous amounts of information that were stored until recently in libraries and archives not sufficiently accessible to the average user is a matter of utmost importance to ImageStore Systems Ltd. We are confident that this work will help preserve this important archival material for our benefit and that of future generations”.