(Post by Seth M. Rodriquez)
“What do you know about the biblical city of Zarephath? Where is it mentioned in the Bible? What biblical events happened there?” It is a well-known fact that while teaching or preaching, it is helpful to start your dialogue by asking questions that will gain the attention of your listeners. In addition, in today’s day and age where so much of people’s intake of information is visual, this technique can be even more effective if it is coupled with a picture, such as this one:
Although the photo and the name of Zarephath may not be familiar to most people (even people who are familiar with the Bible), the significance of the place will become evident to your listeners when you connect it with the biblical references to this place. In other words, it becomes a springboard to an important biblical story.
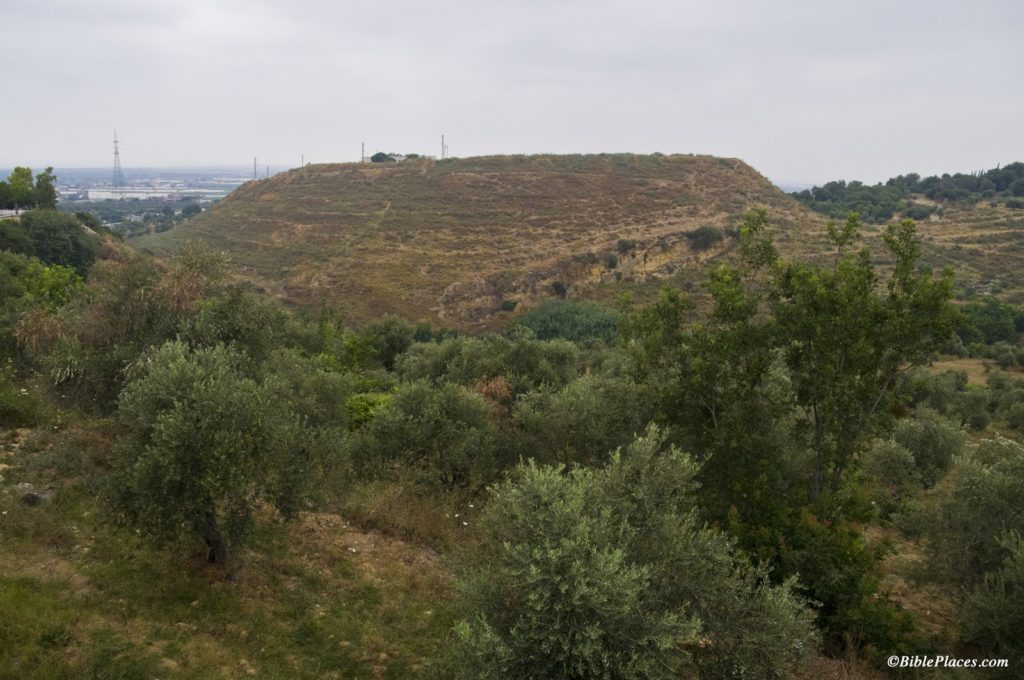
This week’s photo comes from Volume 8 of the revised and expanded edition of the Pictorial Library of Bible Lands, which focuses on Lebanon. The photo is entitled “Zarephath, Phoenician Harbor and Tell from East” (photo ID #: adr090508617). Volume 8 is part of the “expanded” features of the PLBL. It is a completely new volume featuring the pictures of A.D. Riddle, a frequent contributor to this blog.
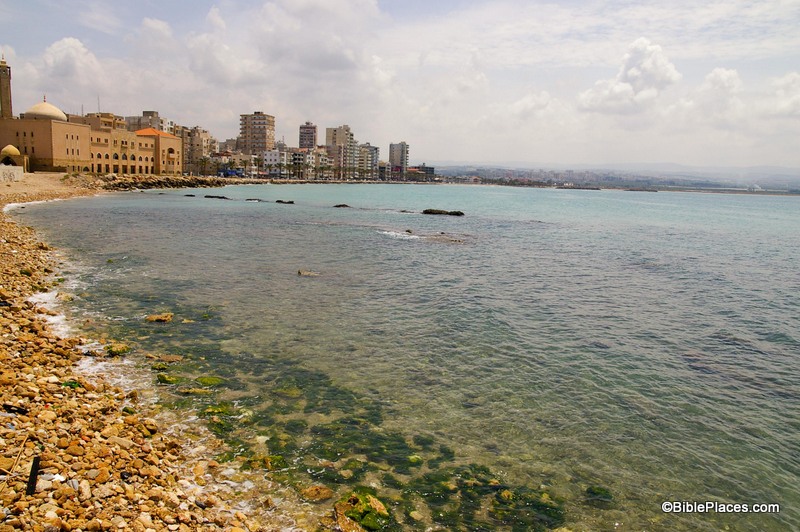
So where is Zarephath and what is its biblical significance? Zarephath is an ancient city on the coast of Phoenicia, about 8 miles (13 km) south of Sidon and 14 miles (22 km) north of Tyre. In antiquity, it had a long and productive existence: it was inhabited from the Late Bronze Period (1600 BC) through the Byzantine Period (AD 600), so it was standing in both Old Testament and New Testament times. There is also a modern village about a mile from the site today. Naturally the name of the town changed over the years and as you moved from one culture to another: it was referred to as “Zarephath” by the Israelites, “Sarpu’uta” by the Egyptians, “Sariiptu” by the Assyrians, “Sarepta” by those in Hellenistic and Roman times, and “Sarafand” today.
Zarephath occurs in two chapters in the Bible: 1 Kings 17 and Luke 4. In the book of 1 Kings, Zarephath is the town where the Lord instructed Elijah to go during the last part of the three-year of drought in Israel.
Then the word of the Lord came to him, “Arise, go to Zarephath, which belongs to Sidon, and dwell there. Behold, I have commanded a widow there to feed you.” (1 Kgs. 17:8-9, ESV)
While he was there, the Lord provided for Elijah, the widow, and her son in a miraculous fashion. This was followed by another miracle when the widow’s son died and the prophet raised him back to life.
The drought ended in the next chapter, 1 Kings 18, after Elijah confronted the prophets of Baal on the top of Mount Carmel. In a way, the events in Zarephath were a subtle precursor to the dramatic confrontation in 1 Kings 18. Zarephath was in the territory of Sidon, the homeland of Queen Jezebel and a region where Baal was worshipped. In fact, Jezebel was the one responsible for making Baal worship the official state religion in Israel after she married King Ahab, as 1 King 21:25-26 makes clear. In light of all this, Elijah’s words to the widow in chapter 17 are significant:
For thus says the Lord, the God of Israel, “The jar of flour shall not be spent, and the jug of oil shall not be empty, until the day that the Lord sends rain upon the earth.” (1 Kgs. 17:14, ESV, emphasis added)
This was a bold claim in the territory of Baal-worshippers: the God of the Israelites will perform a miracle on your behalf, not the god of the Sidonians. The widow herself seems to have already had faith in the God of Israel (1 Kgs. 17:12), but when 1 Kings 17 is studied in context with 1 Kings 18 the theme seems to be that God is mightier than the false god Baal.
Finally, in Luke 4:24-26, Jesus references these events while discussing the fact that a prophet has no honor in his hometown. Jesus was almost stoned after saying this, probably because he used examples where Israelite prophets were used as a means of blessings to Gentiles … a truth that was not very palatable in 1st century Galilee.
This and other photos of the Zarephath are included in Volume 8 of the Pictorial Library of Bible Lands and can be purchased here. More information and photos about Zarephath can be found on the BiblePlaces website here.